In the U.S., navigating the healthcare system can feel overwhelming. Between copays, coverage networks, referrals, and medical jargon, one phrase you’ll come across often is “outpatient services.” But what does it actually mean? And why does it matter?
Outpatient services are a major pillar of modern healthcare. They represent a shift away from long hospital stays and toward efficient, flexible, and more affordable care. This post will break down what outpatient care is, how it works, what it costs, and why it’s reshaping the healthcare landscape in the U.S.
What Does “Outpatient” Mean?
Outpatient care refers to medical services provided without requiring a patient to stay overnight in a hospital or care facility. Patients come in for an appointment, procedure, or treatment and return home the same day.
Common settings include:
These services can range from routine checkups to advanced diagnostics and surgeries that once required hospital stays. Thanks to medical innovation, many procedures are now less invasive and safer, allowing for faster recovery and home-based healing.
Historical Shift: From Hospitals to Ambulatory Care
Historically, hospitals were the central hub for almost all types of medical care. Even minor surgeries and diagnostics often meant at least an overnight stay. But since the 1980s, outpatient care has grown rapidly.
Why?
-
Advances in medical devices and imaging
-
Development of minimally invasive surgical techniques
-
Pressure to reduce healthcare costs
-
Patient preference for quicker recovery at home
Today, over 60% of all surgeries in the U.S. are done on an outpatient basis, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). This shift is not only about convenience—it's about better outcomes, lower costs, and efficient use of resources.
Types of Outpatient Services
Outpatient services vary widely. Here’s a breakdown of common services and their average costs in the U.S.:
Each of these services can be performed without a hospital bed. However, costs can vary by region, insurance coverage, and provider.
Average Cost of Common Outpatient Services in the U.S.
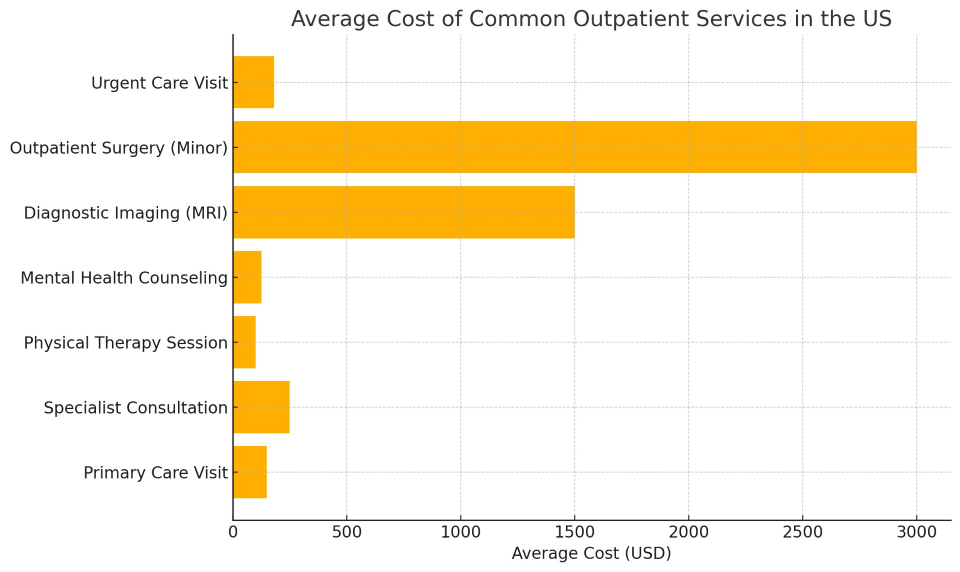
As shown, physical therapy and counseling sessions tend to be more affordable, while imaging and minor surgeries cost significantly more—even on an outpatient basis.
Outpatient vs. Inpatient: What’s the Difference?
Understanding this difference can save you time and money:
Patient Experience: What to Expect
Outpatient care is typically more streamlined. Here’s how a typical outpatient visit flows:
-
Scheduling: You book an appointment or walk in (urgent care).
-
Check-In: Minimal paperwork, often digital.
-
Procedure/Consultation: You receive treatment, imaging, or evaluation.
-
Discharge: You receive aftercare instructions and go home the same day.
-
Follow-Up: May include remote monitoring, telehealth, or follow-up visits.
Many outpatient centers are now designed to feel more like wellness clinics than sterile hospitals, improving the overall experience.
Why Outpatient Care Matters in the US Healthcare System
Healthcare in the U.S. is notoriously expensive. Outpatient services help reduce that burden in key ways:
-
Lower Costs for Patients: Outpatient procedures are generally 30–60% less expensive than inpatient equivalents.
-
Better Insurance Outcomes: Many insurers incentivize outpatient care through lower co-pays or deductibles.
-
Reduced Hospital Strain: Freeing up hospital beds for patients who truly need them.
-
Improved Access to Care: Outpatient clinics often operate evenings or weekends, giving more flexibility to working families.
According to a 2023 Kaiser Family Foundation report, outpatient services account for nearly 45% of healthcare spending by employer-sponsored insurance plans.
Regulation and Quality Control
Outpatient centers are regulated by both federal and state agencies. Key quality oversight bodies include:
Licensing, credentialing, and audits are part of maintaining safe outpatient environments. Many facilities voluntarily undergo accreditation to prove high standards of care.
Future Outlook: Outpatient is the New Normal
Healthcare delivery is moving out of the hospital—and fast.
What’s driving the growth?
-
Telehealth Integration: Follow-ups and counseling can now happen virtually.
-
Wearable Monitoring: Devices allow doctors to track patients remotely.
-
Retail Health Clinics: Pharmacies and stores like CVS and Walgreens are expanding outpatient services.
-
Home-Based Care: Infusions, physical therapy, and even dialysis are now delivered at home.
According to Deloitte, outpatient visits are projected to grow by over 15% by 2030, while inpatient hospital stays are expected to decline by 2–3%.
What You Should Know
Outpatient services are no longer the future—they're the present. They offer a cost-effective, patient-friendly, and scalable way to deliver care across the U.S.
But it's important to understand your own needs:
-
Not every condition can be handled outpatient.
-
Costs vary—ask for estimates in advance.
-
Choose accredited providers to ensure safety.
In a healthcare system where every dollar and every decision counts, understanding outpatient care gives you more control over both your health and your spending.