Veterinary surgery is more than just medical procedures—it’s a cornerstone of animal healthcare in the United States. From routine spaying and neutering to advanced orthopedic repairs, surgery allows veterinarians to dramatically improve the quality of life for pets and animals across the country. This article explores the most common procedures, the cost and recovery expectations, workforce trends, innovations in technology, and the pressing challenges facing this vital industry.
What Is Veterinary Surgery?
Veterinary surgery involves the use of operative techniques to diagnose, treat, and prevent diseases in animals. This spans both soft tissue surgery (e.g., abdominal operations, tumor removals) and orthopedic procedures (e.g., bone fractures, ligament repair). In the U.S., these surgeries are primarily done in private practices, animal hospitals, and specialized surgical centers.
There are three main categories of surgeries:
-
Elective (e.g., spaying/neutering)
-
Necessary but non-urgent (e.g., removal of benign tumors)
-
Emergency (e.g., gastric torsion, trauma)
Most Common Veterinary Surgeries in the U.S.
1. Spaying and Neutering
These are the most frequently performed surgeries in the country. Spaying (ovariohysterectomy) and neutering (orchiectomy) help control pet overpopulation and reduce risks of reproductive cancers. They're also linked to fewer behavioral issues.
-
Cost: ~$200
-
Recovery time: ~10 days
2. Dental Surgery
Pets commonly suffer from periodontal disease. Dental procedures include tooth extractions, gum treatment, and oral mass removals. Poor dental health can cause infections that spread to vital organs.
-
Cost: ~$400
-
Recovery time: ~7 days
3. Tumor Removal
As pets live longer, they’re more likely to develop tumors. Surgical removal is often the first line of defense, especially if the tumor is localized.
4. Orthopedic Surgery
These surgeries are among the most expensive and involved. Common cases include torn cruciate ligaments (like ACLs in dogs), fractured bones, and hip dysplasia corrections.
5. Ophthalmic Surgery
Conditions like cataracts, cherry eye, and glaucoma often require surgical intervention. These are delicate procedures that often restore sight or prevent total blindness.
-
Cost: ~$1,200
-
Recovery time: ~21 days
Average Costs and Recovery Times for Common Procedures
Average Cost of Common Veterinary Surgeries
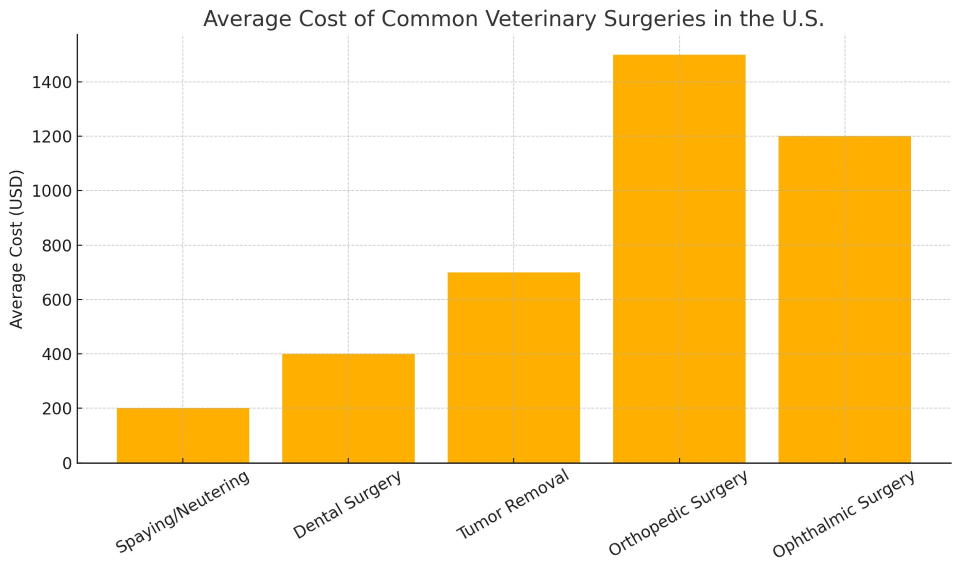
This chart provides a quick visual comparison of the financial impact of each procedure. While spaying and dental care are relatively affordable, orthopedic and ophthalmic surgeries demand significantly higher financial planning.
The State of the Veterinary Industry in the U.S.
-
Market size: $66 billion in 2023
-
Projected size by 2029: $70 billion
-
Veterinary positions (2024): 130,415
-
Female veterinarians: 88,588
-
Male veterinarians: 40,968
-
Nonbinary/undisclosed: 859+
Growth in this industry is largely driven by:
-
An increase in pet ownership (especially during the COVID-19 pandemic)
-
Advances in surgical and diagnostic technology
-
Shifts in societal attitudes—pets are increasingly seen as family members
Technology Transforming Veterinary Surgery
The tools and techniques available to today’s veterinary surgeons are evolving quickly:
-
Laparoscopy & Endoscopy: Minimally invasive tools mean faster healing and less post-op pain.
-
3D Printing: Custom bone implants and prosthetics tailored to an animal’s exact anatomy.
-
Laser Surgery: Reduces bleeding, swelling, and post-op discomfort.
-
Regenerative Therapies: PRP (platelet-rich plasma) and stem cell injections are being used for ligament damage and arthritis.
-
AI-Driven Diagnostics: Artificial intelligence is improving surgical planning and predicting complications with greater accuracy.
Challenges in the Field
While the outlook is largely positive, veterinary surgery faces serious challenges:
1. Rising Costs
The cost of veterinary services, particularly surgery, continues to climb. This is due to:
Many Americans now rely on pet insurance or financing options like CareCredit to manage high costs.
2. Burnout and Mental Health
Veterinary professionals experience higher rates of burnout and suicide compared to many other medical fields. Emotional fatigue, long hours, and client financial pressure are key stressors.
3. Workforce Gaps
Some regions, particularly rural areas, face shortages of skilled veterinary surgeons. This affects access to critical care, especially in emergencies.
4. Legal and Regulatory Complexity
Telemedicine growth has outpaced regulation. Laws on prescribing medication remotely and cross-state licensing vary widely, adding layers of complexity for clinics.
Veterinary surgery is an essential part of modern animal healthcare in the United States. It blends high-tech medical science with compassion and precision. As demand grows, so do the pressures—financial, emotional, and operational. But with emerging technologies, a more robust workforce, and growing public support for quality pet care, the future of veterinary surgery looks promising.
If you’re a pet owner, understanding the procedures, costs, and care involved in veterinary surgery can help you make informed decisions when your animal companion needs it most.