Hospitals in the United States are evolving rapidly—thanks to technology. What was once a place for reactive treatment is now becoming a hub for proactive, connected, and high-tech care. From digital records and telehealth to AI diagnostics and robotic surgery, modern hospitals are redefining how patients are diagnosed, treated, monitored, and even discharged.
This article explores how U.S. hospital services are developing through technology, which tools are seeing the highest adoption, and what patients can expect in the years ahead.
Hospital Technology Implementation Rates
Hospital Technology Adoption Rates in the U.S.
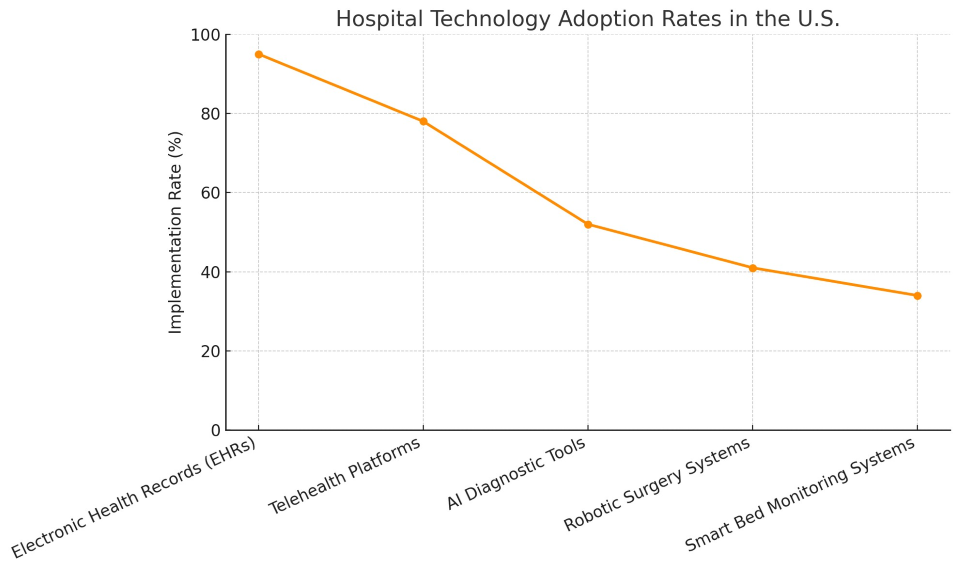
The chart illustrates which innovations are most widely used in American hospitals, with EHRs and telehealth platforms leading the charge and newer tech like AI diagnostics and smart beds gaining ground steadily.
1. Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Adoption Rate: 95%
EHRs are the digital backbone of modern hospitals. They’ve replaced paper charts and made it possible for clinicians to:
-
Access medical history instantly
-
Track lab results in real time
-
Share data securely across departments
-
Send prescriptions electronically
Patient Benefits:
EHR systems like Epic and Cerner are now standard across nearly all hospital systems.
2. Telehealth Platforms
Adoption Rate: 78%
Driven by the COVID-19 pandemic, telehealth has become a permanent part of hospital care models. Patients can now meet doctors virtually via video call, reducing unnecessary hospital visits and easing pressure on emergency departments.
Key Areas:
-
Follow-ups after hospitalization
-
Psychiatry and counseling
-
Pre-op evaluations and post-op check-ins
-
Chronic disease management
Hospitals with telehealth capacity have seen 30–40% fewer unnecessary in-person visits, saving time and reducing exposure risk.
3. AI Diagnostic Tools
Adoption Rate: 52%
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is being used to improve the accuracy and speed of diagnosis. AI platforms can:
For example, AI algorithms can detect lung cancer or diabetic retinopathy earlier than traditional manual review.
Hospitals that integrate AI report not only improved outcomes but also a reduction in diagnostic errors.
4. Robotic Surgery Systems
Adoption Rate: 41%
Robotic-assisted surgery enables minimally invasive procedures with greater precision. The most famous system, da Vinci Surgical System, is now used for:
-
Prostate surgery
-
Gynecological procedures
-
Heart valve repair
-
Bariatric surgery
Advantages:
-
Smaller incisions
-
Less blood loss
-
Shorter hospital stays
-
Faster recovery times
While not yet available in every facility, robotic systems are increasingly common in academic and urban hospitals.
5. Smart Bed Monitoring Systems
Adoption Rate: 34%
Smart beds do more than just support patients. They monitor:
These systems alert nurses in real time and automatically record data into the patient’s EHR.
They are especially useful in ICUs, step-down units, and geriatric wards, improving both safety and staffing efficiency.
Additional Technologies Gaining Ground
Besides the five above, hospitals are exploring:
-
RFID tracking for medical equipment and patient IDs
-
Voice recognition tools for charting and hands-free commands
-
Automated medication dispensers
-
Wearable biosensors for outpatient follow-up
-
Cloud-based analytics dashboards for capacity planning
These tools help streamline workflow, reduce errors, and make hospitals more adaptive to rising patient demands.
The Patient Experience: Faster, Smarter, Safer
Technology isn’t just changing how care is delivered—it’s transforming how patients experience hospitals. Benefits include:
-
Shorter wait times due to digital intake
-
Access to test results via mobile apps
-
Real-time updates during surgery via text
-
Fewer medical errors due to system checks
-
Personalized discharge instructions and digital follow-ups
In tech-forward hospitals, the “smart room” is becoming the new standard.
Training and Workforce Integration
For technology to work, staff must be ready. Hospitals are investing in:
-
Simulation labs to train surgeons on robotic systems
-
Digital literacy for nursing staff
-
Cross-training IT and clinical roles
-
User-friendly interfaces to reduce burnout
Well-trained staff ensure that new tools enhance—not complicate—hospital workflows.
Challenges to Full Integration
Even with promising results, hospitals face obstacles:
-
High cost of implementation and upgrades
-
Resistance to change from seasoned staff
-
Cybersecurity threats
-
System interoperability issues
-
Disparities between rural and urban hospitals
Small and rural hospitals often lack the budget or bandwidth to implement the same tools used in major academic centers.
Policy and Funding Support
Government programs are helping to accelerate tech adoption:
-
HITECH Act: Boosted EHR adoption through incentives
-
FCC Telehealth Grants: Expanded rural access
-
CMS Innovation Models: Encourage data-driven care
-
State health IT programs: Support local system upgrades
Hospitals that embrace these programs gain access to funds and expertise, speeding up modernization.
The Future: AI, Automation, and Precision Medicine
Looking ahead, hospital tech is moving toward:
-
Predictive analytics for early intervention
-
AI-powered discharge planning
-
Precision medicine engines using genetic data
-
Interconnected hospital systems for regional health monitoring
Soon, patients may receive care based on real-time data, personal biology, and AI-assisted insights—making hospitals safer, faster, and more proactive.
Technology is no longer a bonus in hospital care—it’s a necessity. From digital records to smart monitoring, U.S. hospitals are embracing innovation not just to improve efficiency, but to save lives, reduce errors, and enhance the patient journey.
As tools become more advanced and accessible, every hospital—regardless of size or location—has the opportunity to provide high-tech, human-centered care.